When we think about nutrition, we often focus on our intake of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. However, one factor that frequently gets overlooked in discussions about diet is alcohol consumption. From casual social drinking to celebratory toasts, alcohol is woven into the fabric of many cultures and lifestyles. Yet, its impact on our nutritional balance can be important and multifaceted. in this article, we’ll explore how alcohol interacts with the nutrients in our bodies, how it can lead to deficiencies, and why understanding this relationship is crucial for maintaining overall health. Whether you’re a regular drinker or an occasional sipper, gaining insight into how alcohol affects your nutritional balance is key to making informed choices about your diet and well-being.
Table of Contents
- Understanding How Alcohol Impacts Nutrient Absorption
- Identifying the Vitamins and Minerals Affected by Alcohol Consumption
- Strategies for Maintaining Nutritional Balance While Drinking
- Long-term Consequences of Alcohol on Overall Health and Nutrition
- In Summary
Understanding How Alcohol Impacts Nutrient Absorption
Alcohol can significantly hinder the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, leading to potential deficiencies that can impact overall health. When alcohol is consumed, it competes with vitamins and minerals for absorption in the intestines, often disrupting the delicate balance necessary for optimal nutrient uptake. Some nutrients notably affected include:
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): Essential for energy metabolism, can become depleted in alcoholics.
- Folate: crucial for DNA synthesis and repair; alcohol interferes with its metabolism.
- Vitamin B12: Critically important for nerve function and the production of DNA; absorption is compromised.
- Magnesium and Zinc: These minerals play vital roles in numerous bodily functions and are frequently enough lower in individuals who consume high amounts of alcohol.
Furthermore, alcohol can alter liver function, which is critical for metabolizing nutrients and detoxifying harmful substances. A compromised liver may lead to a reduced production of bile, necessary for fat digestion and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K. This disruption may initiate a cascade of health issues, making it essential to be mindful of alcohol intake, especially for those aiming to maintain a balanced nutrient profile. Increasing awareness about these effects can empower individuals to make informed choices regarding their dietary habits and alcohol consumption.
Identifying the Vitamins and Minerals Affected by Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption can significantly impact the levels of essential vitamins and minerals in the body, disrupting the delicate nutritional balance necessary for overall health. Some of the key nutrients affected include:
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): Alcohol interferes with its absorption, leading to potential neurological issues and exhaustion.
- Vitamin B6: chronic drinking reduces the availability of pyridoxine, essential for protein metabolism and cognitive function.
- Vitamin B12: Abnormal absorption may result in anemia and neurological complications due to damaged intestinal lining.
- Folic Acid: Alcohol inhibits folate absorption, which is crucial for DNA synthesis and cell division.
- Magnesium: Excessive intake can cause a depletion of magnesium levels, affecting muscle function and energy production.
Moreover, alcohol not only affects the bioavailability of these nutrients but also induces alterations in the liver, a vital organ in nutrient metabolism.The consequences can lead to deficiencies that manifest as various health problems.key minerals that may experience depletion include:
- Zinc: Necessary for immune function and wound healing, its levels can drop significantly with heavy drinking.
- calcium: Alcohol may disrupt calcium absorption, affecting bone health and increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Potassium: Fluid imbalance induced by alcohol consumption can lead to hypokalemia, which can be dangerous for heart health.
Strategies for Maintaining Nutritional Balance While Drinking
maintaining nutritional balance while enjoying alcoholic beverages requires a proactive approach. First and foremost,prioritize hydration. Drinking water before, during, and after alcohol consumption can definitely help mitigate dehydration, which can impact your overall well-being. Incorporating drinks like sparkling water or herbal teas alongside cocktails can also add flavor without excess calories.It’s essential to choose quality over quantity; opt for drinks made with fresh ingredients and avoid sugary mixers that can spike your caloric intake and disrupt your nutritional goals.
Additionally, consider your meals carefully when planning to drink. Healthy snacks and meals rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats can help stabilize your blood sugar levels and reduce the impact of alcohol on your system. Foods such as nuts, lean meats, and whole grains can effectively support your body. Furthermore, planning your drinking occasions can be beneficial; aim for moderation by limiting consumption to special events and ensuring that you have alcohol-free days throughout the week. This balance fosters a healthier lifestyle while still allowing room for enjoyment.
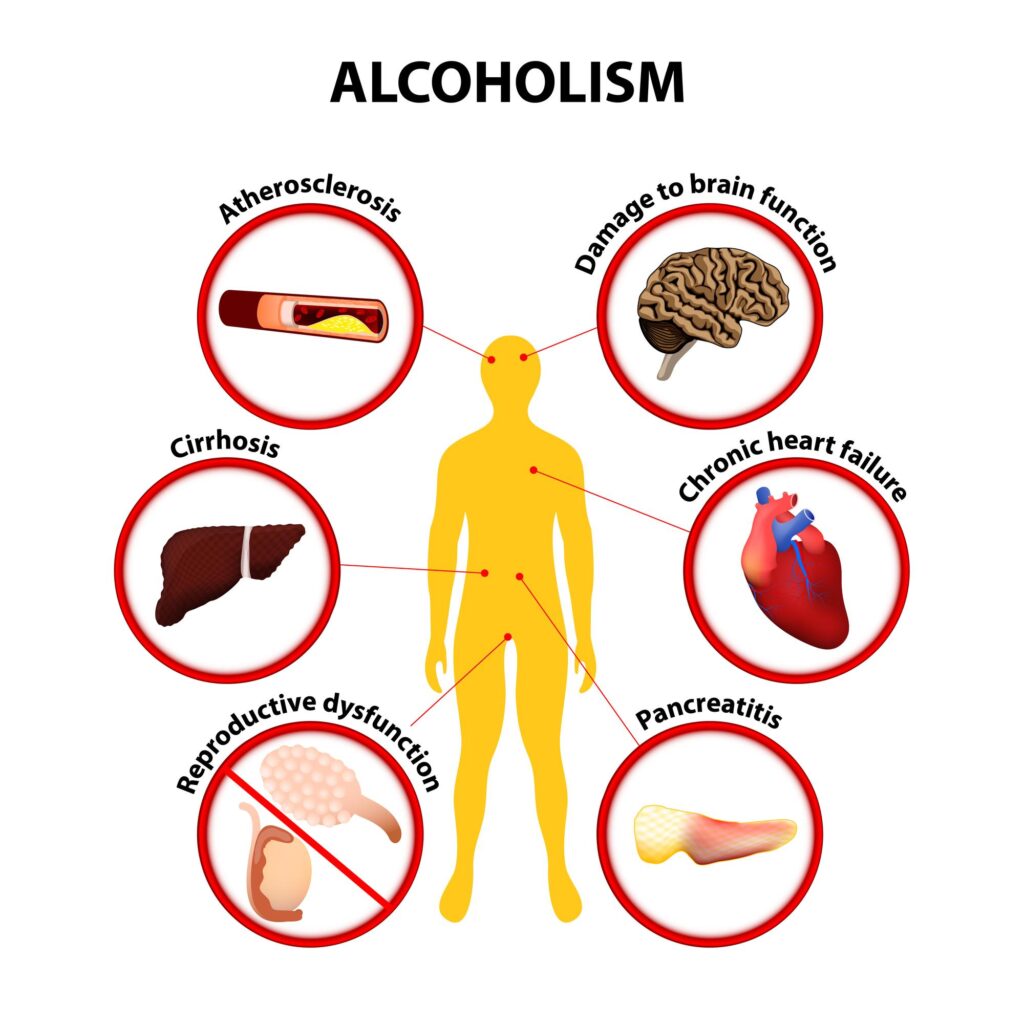
Long-term Consequences of Alcohol on Overall Health and Nutrition
Alcohol consumption has far-reaching implications for overall health, particularly when it becomes a long-standing habit. Beyond the immediate effects, chronic drinking can lead to a series of nutritional deficiencies that compromise bodily functions. Here are some of the most significant long-term consequences:
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Regular alcohol intake disrupts the absorption of vital nutrients, particularly B vitamins.
- weight Gain: Alcohol is calorie-dense but nutrient-poor,leading to excessive caloric intake without providing the necessary nutrients.
- Liver Damage: The liver struggles to metabolize alcohol, which can lead to fatty liver disease and eventually liver failure, affecting nutrient metabolism.
- Dental Health Issues: Alcohol can contribute to gum disease and tooth decay, hindering the ability to eat a balanced diet.
The impact of alcohol on mental well-being also plays a crucial role in nutritional balance.Chronic alcohol use is linked to depression and anxiety, which can diminish motivation to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including proper eating habits. This creates a vicious cycle where poor dietary choices exacerbate mental health issues. Consider these points for a complete understanding:
- Reduced Appetite: Alcohol can suppress hunger signals, making individuals less inclined to consume balanced meals.
- Impaired Judgment: Intoxication can lead to poor decision-making around food choices, often resulting in reliance on fast food or unhealthy snacks.
- Increased Cravings: Alcohol can stimulate appetite for high-calorie,low-nutrient foods,further impacting nutritional balance.
In Summary
understanding alcohol’s effects on nutritional balance is crucial for making informed choices about our health. While moderate consumption may not significantly disrupt nutritional status for everyone, it’s clear that alcohol can influence our dietary habits, metabolism, and overall well-being.By recognizing how alcohol interacts with nutrients and impacts our bodies, we can better navigate our choices and prioritize our health. Whether you’re considering a night out or simply re-evaluating your daily routine, being aware of these dynamics can empower you to make decisions that align with your nutritional goals. Remember, balance is key, and informed choices lead to a healthier lifestyle.Cheers to that!